Androgenetic Alopecia
Causes of Androgenetic Alopecia
There are many causes of hair loss. In the case of most men with hair loss the condition is hereditary. The genes for male pattern baldness can be inherited from either side of the family. The medical term for male pattern baldness is Androgenetic Alopecia. This type of hair loss is caused by the hormone Dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Myths about Androgenetic Alopecia
There are many myths about the causes of hair loss. It is most definitely NOT caused by poor circulation, clogged hair follicles, mites, shampooing too often or wearing hats and helmets. A healthy diet can improve the quality of hair, but not the quantity. Stress alone does not usually cause hair loss.
Cures for Androgenetic Alopecia
There is no scientifically proven cure for androgenetic alopecia.
Androgenetic Alopecia treatment options
The FDA is the Food and Drug Administration in the US. It has approved two medicines to treat androgenetic alopecia. They are most effective when used together. This medical treatment for hair loss has been successful for many of our patients.
Hair transplant surgery is a permanent treatment for patients with androgenetic alopecia. The hair that is transplanted is not affected by the balding process. It is taken from the back and sides of the head which are unaffected by the condition. The transplanted hair, once established, will normally remain on the patient’s head for the rest of their life.
FAQ Videos
Alopoecia Areata

Alopecia Areata (AA) is a hair loss condition. It most commonly affects scalp and beard hair but can also affect other areas of hair on the body.
A large proportion of those suffering from AA have a family history of the condition. This is particularly true for those who are affected early on.
While the cause in not currently known, AA is generally believed to be an autoimmune disease. Many who suffer from it also suffer from other autoimmune diseases such as ulcerative colitis.
AA affects 0.1-0.2% of the population at any one time. It has a lifetime risk of 1.7%. 60% of patients experience their first episode under the age of 20. Patients often present with a sudden episode of hair loss, usually in round or oval patches. Sometimes the whole scalp or even the whole body hair may be lost.
Alopecia Areata – Treatment Options
Early treatment is advisable. Patients are advised to consult their GP as early as possible.
Speak to a surgeon today about your treatment options
Many treatment options for AA have been developed. This can include a course of steroids, the use of topical Minoxidil or phototherapy. No one treatment is effective in all cases. Some individuals may show no response to any treatment.
Early treatment is advisable. Patients are advised to consult their GP as early as possible for referral to a clinical dermatologist or immunologist.
Hair Transplant Surgery as a treatment for AA
Hair transplant surgery has little, or no, role in the treatment of this condition. This is because the transplanted hairs are destroyed by the same process. Therefore, the results do not last.
If the process is no longer active, persisting areas of hair loss can be successfully treated with hair transplantation. It is difficult to confirm with any certainty when the process is no longer active. As a result, hair transplant surgery in these cases is rare.
Post-Operative Instructions

Home care information for patients following hair transplant surgery
Dr. Maurice P. Collins
F.R.C.S.I., D.L.O., F.R.C.S.Ed, F.R.C.S.
Hair transplant surgery is a delicate procedure. Your adherence to these post-operative instructions is essential for optimal results. It is our aim that you are pleased with the care you receive, and we encourage you to contact us with any problems or questions. If you have any problems following the surgery please call HRBR’s office number below. If the office is unattended and you have an urgent problem, please contact the mobile number of your attending surgeon.
Office hours contact (8a.m. – 5p.m.):
E-mail: info@hrbr.co.uk
Post- Operative Care
Immediately Post OP
- A spray bottle and a water solution are supplied on discharge. You may use tap water when the solution provided is finished.
- You will need to spray the transplanted area and the donor every 20 minutes for the first 12 hours. When doing this put some towels around your shoulders and let all the water drip down
- You will need to spray vigorously, use both hands to ensure that you cover all the transplanted and donor area. Do not touch the transplanted hair
- Once you have completed the 12 hours of spraying you should sleep for a few hours
- Drink plenty of water during this time and eat as normal
- You may store the 1L solution bottle in the fridge
- Premedication is given during surgery and it is important that following your procedure you do not drive and that you are accompanied by a responsible adult on leaving the clinic.
Day 1 to day 3
- On day 1 (day after the surgery) to day 3, you should spray half hourly during your waking hours and sleep as normal at night
- You may use tap water when the solution provided is finished
- Spraying prevents any scab formation on the transplanted area and on the donor area. The transplanted grafts also need to be kept hydrated throughout this period, this is essential for their survival
Day 4- Day 14
- You will commence a tea tree shampoo regime on day 4
- Fill a clean bowl with tepid water, put 10 mls of shampoo in and mix it up to make it quite soapy and with a cup or bowl, pour the solution over the transplanted area and the donor area, and rinse off any soapy solution. You may pat it gently with a clean towel
- This should be done once a day from day 4 up until day 14
- Note: Do not stand under a power shower and
- You may continue spraying the donor area during day 4 to 14 to relieve any itchiness. You may keep the spray bottle in the fridge
- Your stitches (if applicable) will need to be removed between day 7 and day 10. It is advisable to return to HRBR to have these removed
- For FUE patients please attend the clinic for a post-operative check appointment two weeks post op
- FUE patients may occasionally develop yellow crusting on the recipient area approximately 7 – 10 days post op. This is not a cause for concern and will resolve after day 14
- It is advisable to start using Regaine after day 14 to enhance the growth, this should be used at night only on the transplanted area and this can be used for 6 months or continuously post operatively
Day 14 and after
- You may return to your normal hair washing regime, finish using the tea tree shampoo, return to your previous shampoo, wash the hair vigorously using both hands this will remove any crusts in the area. At this stage you may get your hair cut, colour your hair and resume using products like gels and hair sprays. For FUT patients we recommend a scissor cut only.
- It is recommended to avoid strenuous physical activity for 4 weeks post operatively for FUT (2 weeks for FUE); you should avoid gym work, swimming, cycling, tennis, golf, any heavy lifting, strenuous hill walking. This is to avoid any stretching of the scar
- When you return to physical activity you should start off lightly and build up slowly to your previous activity levels
Patients may experience the below immediately following surgery;
- Swelling: This can usually occur 24 to 48 hours after the surgery. You may notice some swelling in the forehead, which may travel down towards the eyelids. This swelling maybe asymmetrical. This will resolve itself, without intervention, usually 48 to 72 hours after it begins.
- Bleeding: there may be some bleeding directly after the surgery from the donor area, if any bleeding occurs, it is important to apply pressure with some gauze for as long as it takes to settle
- Pain: sometimes pain can occur in the donor and the transplanted area, Solpadine and Nurofen are recommended for this, and you can take these alternating every 3 hours. Please see specific instructions about pain relief provided
- Numbness/ tingling sensation in the recipient area sometimes occurs, this will resolve without intervention. It can last from weeks to months
- Infection: There is a very slight risk of infection as with any surgery. You should return to the clinic if you feel there is any signs of infection such as localised redness, or pain
For Your Information
- It is important to note that the transplanted hair will be fully embedded after day 14, that is why you can resume your normal activities at this stage
- The transplanted hair will begin to fall out, usually 2 to 4 weeks after the surgery. You will start to see the hair grow from 6 months after the surgery, this hair will be very fine and minute at first
- At 9 months 70% the hairs will have appeared, however they won’t be fully grown, it will take up to 18 months for full growth to occur
- Shedding of the native hair can also sometimes occur post operatively. This is quite rare and if it occurs it will always re-grow
Note on going on holidays post operatively
- It is possible to go on holidays after the surgery, it is important not to get a sun burn on the scalp as this will damage the skin. Do not swim in swimming pools with chlorine in the first 14 days as the chemicals may damage the grafts, it is however safe to swim in the sea in the first 14 days
- Do not dive
- After day 14 you can swim in swimming pools and apply sun lotion to the scalp and wear a hat if needed. It is advisable to always wear a cap in the sun after day 14. If you are in the sun prior to day 14, you must sit under an umbrella and avoid sitting in direct sun light for long periods
Office Hours Contact:
telephone: +353 1 2091000
e-mail: info@hrbr.co.uk
Pre-Operative Instructions

We advise patients to attend a pre operative appointment prior to surgery, this allows the nursing team to do the following:
- Design planning
- Assessment of your donor hair
- Medical assessment
These are all important aspects in preparation for hair transplant surgery with HRBR.
Please bring a list of any medications you are taking to this appointment.
This appointment will provide you the opportunity to discuss your surgery in more detail, any questions you may have will be answered. All instructions relating to your surgery will be given at this appointment.
Prior to surgery patients should do the following:
- For patients undergoing an FUT procedure keep 2-3 cm length in your hair prior to the surgery, this will ensure the stitches will be hidden post operatively
- For all patients we recommend commencing flexibility exercises in advance of your procedure, please see the HRBR website for instructions – Please ensure to focus on both the back and sides of the scalp. Scalp Massage
- For patients undergoing an FUE procedure please note in most cases the entire head must be shaved to a blade 0 on the day of the procedure
- Stop using Regaine 1 day before
- You can continue taking Finasteride and oral Minoxidil (Loniten) as normal (if prescribed).
- Please stop taking any vitamins and supplements 1 week before
- Start using Tea-Tree shampoo 1 week before your surgery. This is available in all pharmacies and any brand of tea tree shampoo is suitable
- A pre-medication of allopurinol 300mg and valium 5mg should be taken between 6pm and 7pm the evening before your surgery and you should be in for the evening either at home or at your hotel before it is taken.
- This is normally provided to you at your preoperative appointment; however you may need to collect this pre-medication during office hours if you have not already received it.
- Do not drink alcohol for 48 hours before your surgery
- Eat a substantial breakfast before you arrive
- Please read your consent form before you attend for surgery
- Please contact the nursing staff with any queries you have
- Premedication is given during surgery and it is important that following your procedure you do not drive and that you are accompanied by a responsible adult on leaving the clinic.
Scalp Massage

The only limiting factor for a hair transplant is the amount of available donor hair each patient has. The number of grafts that can be taken during a Follicular Unit Transplantation “FUT” transplant is affected by the flexibility of the scalp in the donor region, i.e. at the back and sides of the head. The more flexible the scalp, the easier it is for the surgeon to close the suture line. This means that it should heal better and should result in a smaller scar.
We recommend that patients undergoing an FUT procedure carry out a scalp massage twice a day for as long as possible prior to the procedure.
This video demonstrates the scalp massage technique. If you have any questions about scalp massage, please do not hesitate to contact the clinic.
Scalp Massage Technique
Hair Classification
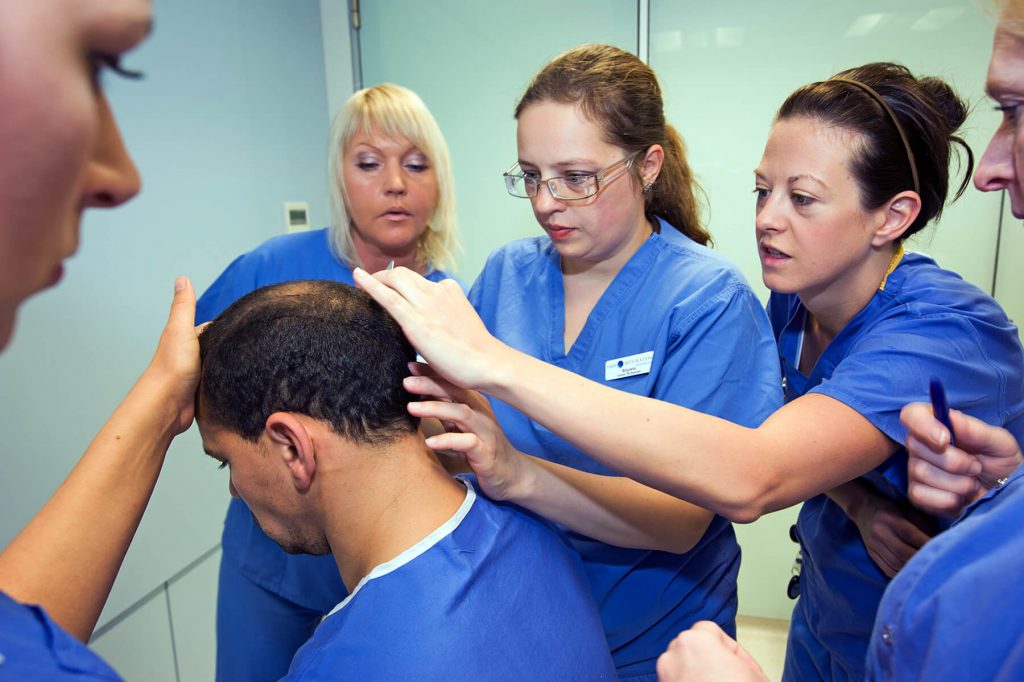
The Norwood Classification
A system of hair loss classification is a useful way to help doctors compare patients. The Norwood Classification is the most commonly used for male pattern baldness.
There are two basic patterns, the most common of which is where hair loss starts in two different areas – the temples and the crown of the head.
Less common patterns feature the hair loss progressing from the front to back.
Non-genetic hair loss from other causes usually follows a completely different pattern again.
Overall Bryan is absolutely delighted that he went ahead with the procedure which was a big decision for him at the time
Bryan Robson
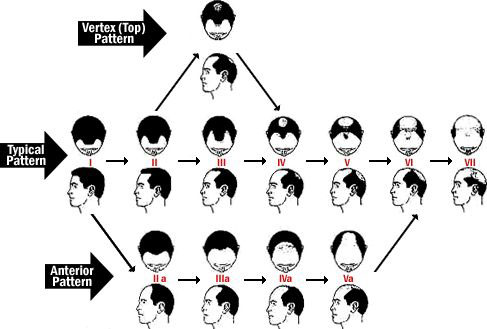
Explanation of Classifications
The Norwood Classification is a system of hair loss classification is a useful way to help doctors compare patients
Speak to a surgeon today about your treatment options
Type I
- No recession
- “Adolescent” hairline
Type II
- Temporal recession less than 2.5cm
- Mild recession along frontal hairline
- “Mature” hairline
Type III
- Further frontal hairline recession
- Deeper recession at corners, “zipper” opening
- Primary stage of balding
Type III Vertex
- Hairloss predominantly in vertex (crown)
- Frontal hairline recession may be present
Type IV
- Further frontal hair loss and temporal recession
- Enlargement of crown (bald spot)
- Solid band of hair across top separating the frontal area from the crown
Type V
- Frontal and temporal balding areas enlarge even further
- Band separating the two areas becomes narrower and less dense
Type VI
- Frontal and crown balding areas merge into one and increase in size
Type VII
- Only a narrow horseshoe band of hair remaining
- Low hairline in the back
- Hair in permanent zone may be sparse
Type A Variant
- Frontal hairline recession keeps advancing backwards
- Single area of balding
- Eventual extent of balding tends to be more limited than in regular Norwood classes
Type IIa
- Entire frontal hairline recedes
Type IIIa
- Frontal hair loss extends to the mid scalp
Type IVa
- Hair loss moves past mid scalp area
Type Va
- Hair loss extends towards the crown
- Back part of the bald area is narrower than in the regular Norwood VI
Hair Shedding “Effluvium”
What is Effluvium?
The medical term for the shedding of hair is Effluvium or Telogen Effluvium. It can be caused by factors such as childbirth, crash diets, thyroid conditions, drugs and anaemia.
The condition is usually temporary and is best treated by a qualified dermatologist.
Why can some hair fall out after a hair transplant?
About 3 weeks after surgery it is normal for patients to experience some shedding of the hair that has been transplanted. This is perfectly normal and nothing to be concerned about. The transplanted hair roots become temporarily dormant. This usually only affects the hair that has been transplanted. The new hair will usually start to appear 4-6 months after a transplant. The full effect of the transplant can be seen about 12 to 18 months post-surgery.
Shedding of hair that has not been transplanted is rare. It is more common in female patients than in male patients. This shedding is temporary and will resolve itself.
What can be done to avoid shedding following a hair transplant procedure?
The team at HRBR have years of experience in caring for patients following their hair transplant. In our experience the use of Minoxidil 5% foam, before and after surgery, can reduce the rate of shedding after the procedure.
Complications / Risks

FAQ – What are the risks of hair transplant surgery?
Hair transplant surgery is an extremely safe out-patient procedure
Speak to a surgeon today about your treatment options
Does hair transplant surgery result in scarring?
Whenever human skin is cut, it heals itself through a process called “fibrosis”, commonly known as scarring. The healing sites around the transplanted hairs are tiny . They are virtually undetectable even on close inspection. Hair Transplant procedures at HRBR are designed to produce a very natural look.
The degree of scarring in the area where the hair is taken around the back and sides of a patient’s scalp depends on several factors. The patient’s own ability to heal, the skill of the surgeon carrying out the transplant and the technique used. For FUT procedures a fine linear scar will be left, for FUE procedures numerous small circular scars will be left. Any clinic claiming to have a scar free procedure should be viewed with caution. It is not possible to cut the human skin without leaving some scar as this is how the human body heals.
What are the potential side effects or complications of hair transplant surgery?
There can be some minor temporary complications or side effects associated with hair transplant surgery. They are as follows: Swelling; Bleeding; Pain; Numbness; Infection; Thinning of Pre-Existing Hair; Hiccups; Itching; Keloid Scarring; Cysts and Lost Grafts.
Swelling
Some mild swelling may occur after the procedure. This is normal. Very rarely, there can be swelling of the forehead for a couple of days after the transplant. Even more rarely, there can be enough forehead swelling that it then causes swelling and bruising on the lower eyelids. This “black eye” develops in roughly 1% of cases and occurs two to four days after surgery. In the unlikely event you suffer from excessive swelling please contact the clinic.
Bleeding
Slight bleeding may occur after surgery around the stitches in the donor area. If it does, keep your head elevated and place some gauze on the area. Apply constant pressure with the palm of your hand for up to 10 minutes. Persistent bleeding occurs in roughly one in a few hundred cases.
If a graft is dislodged, the incision site might bleed. Should this happen, apply pressure to the area with a tissue. If these efforts do not stop the bleeding please contact the clinic.
Pain
Some mild discomfort may occur. If necessary, it can be controlled by the pain medication provided at the end of the surgery. Having said this, half of our patients do not tend to require any pain relief. Those who do take Solpadeine or Panadol for a few days following the hair transplant.
Numbness
Some temporary numbness is inevitable. It is usually experienced around the donor area or graft sites. It generally lasts from three to 18 weeks. However, it is rarely troublesome or long-lasting.
Infection
Developing an infection following hair transplantation at HRBR is highly unusual due to the high standards in place at the clinic. This is only likely in one in several hundred cases. It is easily treated with antibiotics. If any significant redness, tenderness or local pain is noticed please contact the clinic.
Thinning of Pre-Existing Hair
Although rare, some pre-existing hair can thin following surgery. This is temporary and it will return to normal, full condition within a few months. Learn more about “effluvium”.
Hiccups
Hiccups occur after surgery in approximately 5% of cases and usually last from several hours to several days. The cause is unknown.
Itching
Some degree of itching is common with hair transplantation. It is rarely troublesome and lasts only a few days. Spraying the area in the initial few days and then shampooing the hair daily will help the discomfort.
Keloid Scarring
“Keloid scarring” is an abnormal scar that grows beyond the boundary of the original site of a skin injury. It is a raised and ill-defined growth of skin in the area of damaged skin. It only occurs in pre-disposed individuals, and even more rarely (1 in 1,000 cases) can this scarring cause a ridging effect.
Cysts
When many grafts have been transplanted one or more cysts may develop. Cysts usually disappear by themselves after a few weeks. They can also be treated quite effectively. They are generally no more than 2 or 3mm in diameter, similar in size to small pimples.
Lost Grafts
The odd graft may be dislodged accidentally and fall out. This will not significantly affect the overall result of your hair transplant.